An Employer’s Guide to Right to Work Share Code
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
Right to work checks are a fundamental legal requirement for all UK employers. These checks are designed to ensure that all employees have the legal right to work in the UK, securing statutory excuse from penalty for employers and safeguarding the workforce from illegal employment practices. Failure to conduct these checks properly can result in fines up to £20,000 per illegal worker, reputational damage, and in severe cases, criminal convictions.
To streamline the process of checking an employee’s right to work in the UK, the government established the Home Office Online Right to Work Check. In this method, employers can check a candidate’s right to work status via a “share code.” Learn more about it here.
What is a Right to Work Share Code?
Introduced as part of the digitalisation of the immigration system, a share code is a unique 9-character alpha-numeric code provided by the UK government to migrant workers.
This code allows employers to access up-to-date information about an individual’s right to work - securely on a government website.
This process not only minimises the administrative burden but also reduces the risk of document forgery, ensuring a more secure and reliable compliance environment.
{{background-checks-and-the-future-of-hiring="/components"}}
Whom Can Employers Ask a Share Code From?
Right to work checks must be conducted on all employees; however, not every employee will be able to generate a share code. As employers, please remember that share codes can be generated by candidates who:
- Have a pre-settled or settled status from the EU Settlement Scheme
- Have indefinite leave to enter and remain
- Are a Commonwealth citizen with a right to abode
- Have limited leave to remain
A candidate won’t be able to give you a share code if they are:
- A British or Irish citizen, in which case, to check for their right to work, you can ask for their passport OR two other valid documents
- An asylum seeker, in which case they may not have the right to work except for some circumstances
Remember: do not skip right to work checks, even for casual or temporary employees or voluntary workers.
{{background-checks-and-the-future-of-hiring="/components"}}
What Can Employers Know from a Right to Work Share Code?
With a share code and the candidate’s date of birth, employers can readily see the following information:
- The types of job they can and cannot engage in the UK
- For how long they are legally allowed to work in the country.
- The number of hours they are allowed to work (eg. in the case of students)
- Their rights and benefits while working in the UK
- Any access to government services, such as NHS
- Their ability to open a bank account or apply for any credit in the UK
These pieces of information makes it easier for employers to check if the candidate they are considering for a job is indeed legally permitted to carry out the role in the UK.
.jpg)
What To Do After Obtaining the Share Code from the Candidate?
The applicant may give you the share code directly or use an email service to send it to you. Once you have it, you can proceed to the Right to Work Service.gov.uk and enter the share code along with the applicant’s date of birth.
This will direct you to the page showing the candidate’s photo and right to work details.
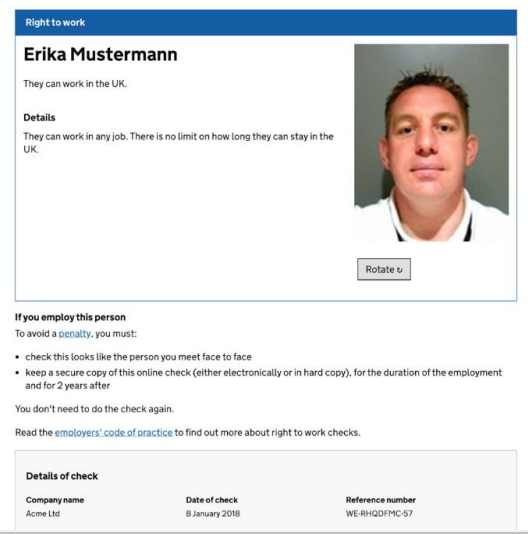
Below the right to work status are listed instructions on how to avoid penalty (gain statutory excuse) should you decide to employ the person. Here’s an example of the list of instructions:
If you employ this person
To avoid penalty you must:
- Check this looks like the person you meet face-to-face
- Keep a secure copy of this online check (either electronically or in hard copy) for the duration of the employment and for two years after
- Get and keep details of their academic term and vacation times
- Do this check again when their visa expires on 19 November 2023
In other words, viewing the right to work status is not enough to gain a statutory excuse. In general, you must still do the following:
- Check if the person in the photo is indeed the candidate you are considering to hire, which means that information truly relates to them.
- Retain the evidence of the check (download the page or make a physical copy) and store it securely for the duration of the employment and for two years after.
- Follow additional instructions as listed in the status page
If ever you know or have reasonable grounds to believe that the person doesn’t have the right to work, and you employ them anyway, remember that you may be found guilty of a criminal offence.
{{background-checks-and-the-future-of-hiring="/components"}}
Advantages and Challenges of Right to Work Share Code for Employers
The Right to Work Share Code system, introduced by the UK government, has significantly streamlined the verification process for employers. However, like any system, it comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Advantages:
- Efficiency in Right to Work Verification: The share code allows employers to quickly access an employee's right to work information online, significantly reducing the time spent on manual document checks.
- Reduced Risk of Fraud: As the details are provided directly by the Home Office, the risk of accepting forged documents is greatly minimised.
- Up-to-Date Information: Employers access the most current information about an employee’s right to work status, which is especially beneficial in cases where immigration statuses might change.
Disadvantages
- Limited Applicability: Not all employees can generate a UK share code. This requires employers to still maintain familiarity with and processes for physical document checks.
- Limited Understanding: While the right to work share code system is quite straightforward, many employees - particularly those who aren’t a confident English-speaker - may struggle with slightly different wordings which point to the same thing (eg. demonstrate right to work, get a share code)
- Risk of Complacency: Employers may become complacent with share codes, mistakenly believing that viewing right to work status is sufficient, when in fact, additional verification steps are necessary to fully establish right to work and secure statutory excuse.
Alternative Methods for Right to Work Checks Beyond Share Codes
As mentioned earlier, not all applicants can generate the right to work share code. Besides using a share code, the Home Office also permits the following methods:
- A right to work check using IDVT via the services of an IDSP
- Manual right to work check
Right to Work Check Using IDVT
Identity Document Validation Technology (IDVT) is an option to check the right to work of a British or Irish citizen who holds a valid passport. The Identity Service Provider (IDSP), such as Veremark, then takes charge of verifying the documents to prove the individual’s right to work.
Note however, that you shouldn’t treat those who don’t hold a valid passport or those who don’t wish to get their documents verified by an IDSP less favourably.
Manual Right to Work Checks
For manual right to work check, here are the documents you need to physically verify:
Helping Candidates: Step by Step Guide on How to Generate the Share Code
If your candidate needs help generating their right to work share code, you may share with them the following information:
- The website where they can view their immigration and work status and generate a share code: https://www.gov.uk/view-prove-immigration-status
- Things they need to prepare:some text
- Their passport, national identity card, or biometric residence card or permit
- The mobile number and email address they used to create a UKVI Account (a security code will be sent in one of these)
- Their date of birth
- The validity of their share code - it’s only good for 90 days.
- The steps in getting a share code. They are outlined in the website and involve choosing their ID document, inputting its number, entering their date of birth, choosing how to receive their security code and receiving it, viewing their status, and finally, getting the share code.
Here’s an easy to follow flow chart you may share with them:
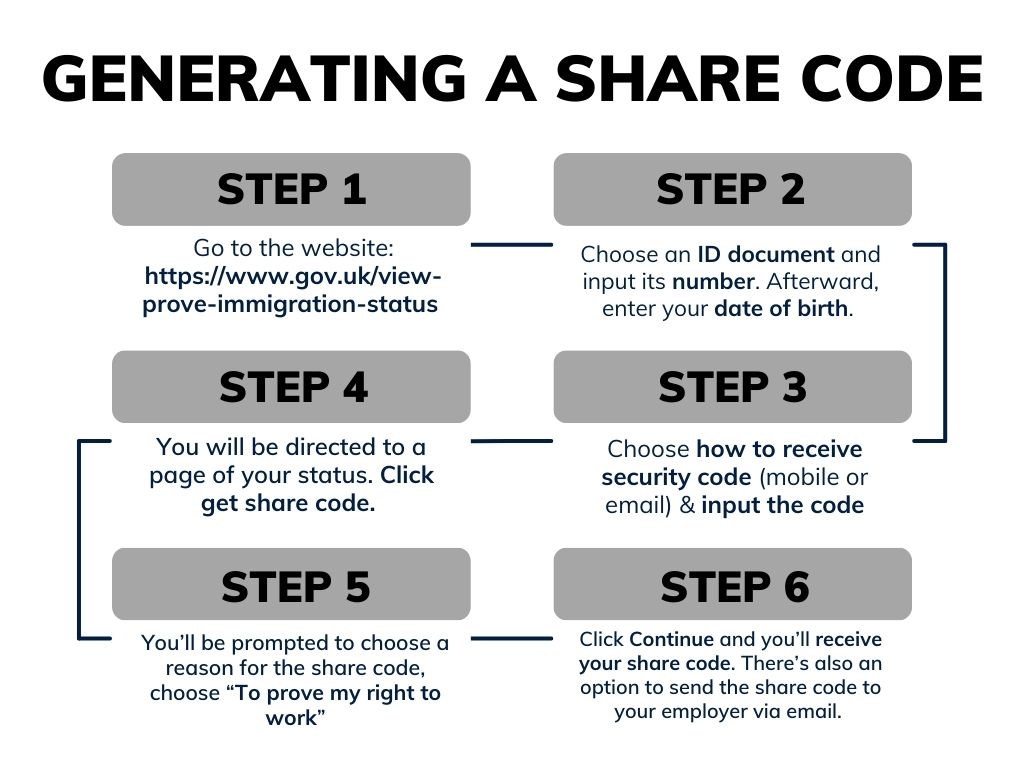
Remind candidates that choosing the correct reason (To prove my right to work) is important to generate the share code correctly. Employers won’t be able to use a share code to check the right to work if it was generated for another purpose.
Of course, inform candidates that you also need their date of birth to conduct the online right to work check.
Partnering with Veremark to Prove a Candidate’s Right to Work
In the UK, employers looking to further streamline the verification of a candidate's right to work can partner with Veremark, an expert in facilitating various compliance checks.
Veremark offers Right to Work Check Services such as Passport checks, ID validation, and Imposter checks, ensuring that each candidate's identity is accurately verified. Additionally, Veremark handles all necessary consent procedures and conducts manual checks in strict adherence to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This comprehensive approach not only simplifies the hiring process but also ensures that all data handling is fully compliant with legal standards.
Conclusion
A right to work share code is a digital confirmation used by employers in the UK to verify a candidate’s eligibility to work. It streamlines the process by providing quick and direct access to the necessary immigration status information through a secure online system. However, while a UK share code offers efficiency, they also present challenges such as reliance on digital access and limited applicability.
As conducting right to work checks is the legal obligation for employers, it's crucial that they exercise thorough due diligence. Beyond using share codes, manual document checks, and ID Verification Technology (IDVT), employers can also collaborate with reputable background screening companies. This partnership ensures comprehensive right to work verification and confirms that candidates are indeed authorised to work in the UK, safeguarding the employer against legal repercussions and fostering a compliant workplace environment.
FAQs
A share code is a unique 9-character alpha-numeric code provided by the UK government to a migrant worker. Employers use the share code to access up-to-date information about a candidate’s immigration and work status.
A share code is only valid for 90 days. After that, the candidate has to generate another unique code.
Using a share code is one of the methods accepted by the government for employers to prove a candidate’s right to work. Done correctly, it’s enough to establish a statutory excuse should an employee be found to be illegally working. Note that viewing a person’s right to work status is not enough - the employer still has to verify their identity, retain the copy of the check securely, and follow several other instructions as per the status page.
Besides the use of a UK share code, an employer can also conduct manual checks by checking physical documents and use an Identity Document Validation Technology (IDVT) for candidates who have a valid British or Irish passport.
FAQs
This depends on the industry and type of role you are recruiting for. To determine whether you need reference checks, identity checks, bankruptcy checks, civil background checks, credit checks for employment or any of the other background checks we offer, chat to our team of dedicated account managers.
Many industries have compliance-related employment check requirements. And even if your industry doesn’t, remember that your staff have access to assets and data that must be protected. When you employ a new staff member you need to be certain that they have the best interests of your business at heart. Carrying out comprehensive background checking helps mitigate risk and ensures a safer hiring decision.
Again, this depends on the type of checks you need. Simple identity checks can be carried out in as little as a few hours but a worldwide criminal background check for instance might take several weeks. A simple pre-employment check package takes around a week. Our account managers are specialists and can provide detailed information into which checks you need and how long they will take.
All Veremark checks are carried out online and digitally. This eliminates the need to collect, store and manage paper documents and information making the process faster, more efficient and ensures complete safety of candidate data and documents.
In a competitive marketplace, making the right hiring decisions is key to the success of your company. Employment background checks enables you to understand more about your candidates before making crucial decisions which can have either beneficial or catastrophic effects on your business.
Background checks not only provide useful insights into a candidate’s work history, skills and education, but they can also offer richer detail into someone’s personality and character traits. This gives you a huge advantage when considering who to hire. Background checking also ensures that candidates are legally allowed to carry out certain roles, failed criminal and credit checks could prevent them from working with vulnerable people or in a financial function.
Trusted by the world's best workplaces






APPROVED BY INDUSTRY EXPERTS
.png)
.png)




and Loved by reviewers
Transform your hiring process
Request a discovery session with one of our background screening experts today.



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
%20(1).jpg)



.png)